As deposits regain value, banks must bolster their deposit management capabilities to ensure they can compete effectively to protect client relationships, profitability, and access to funding.
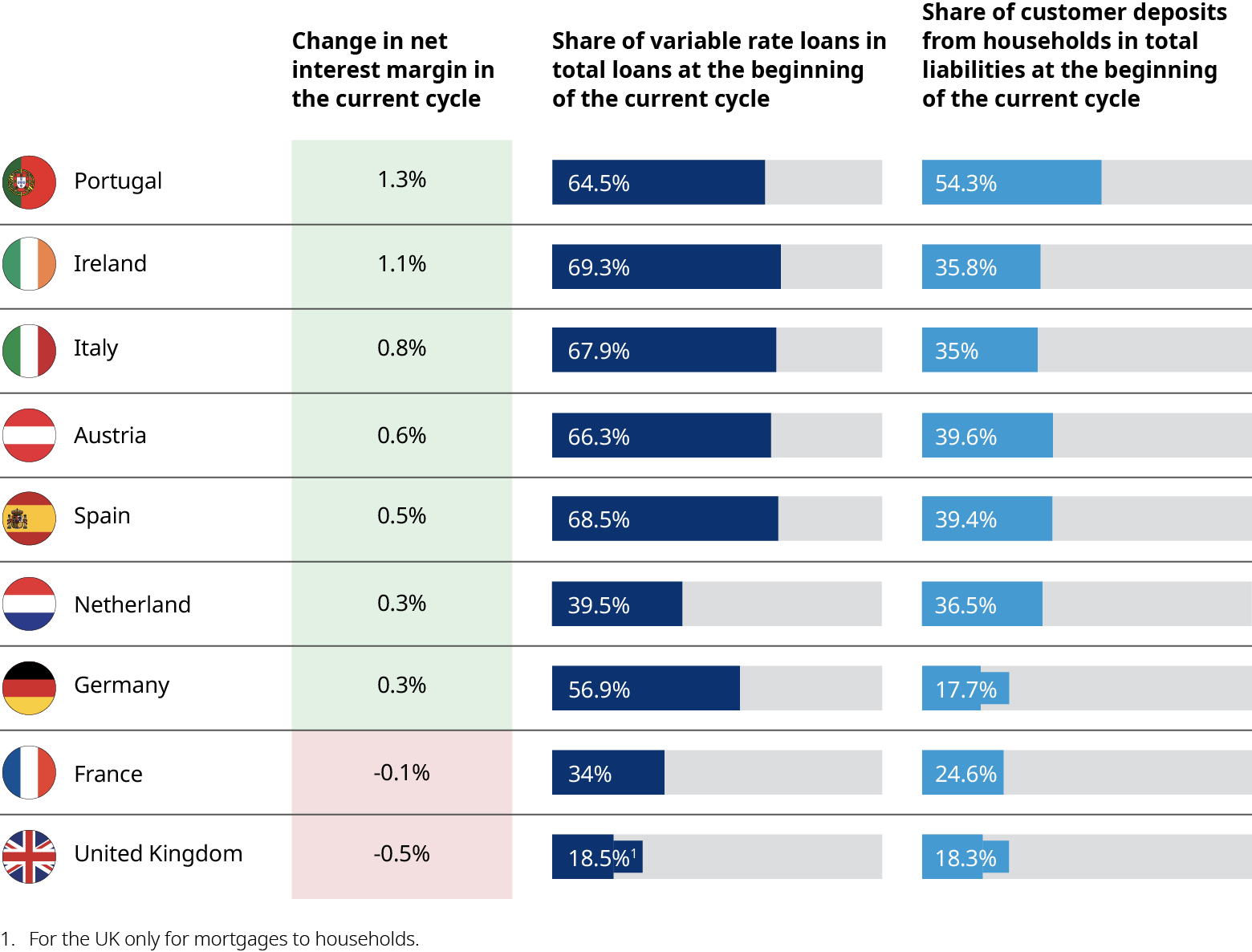
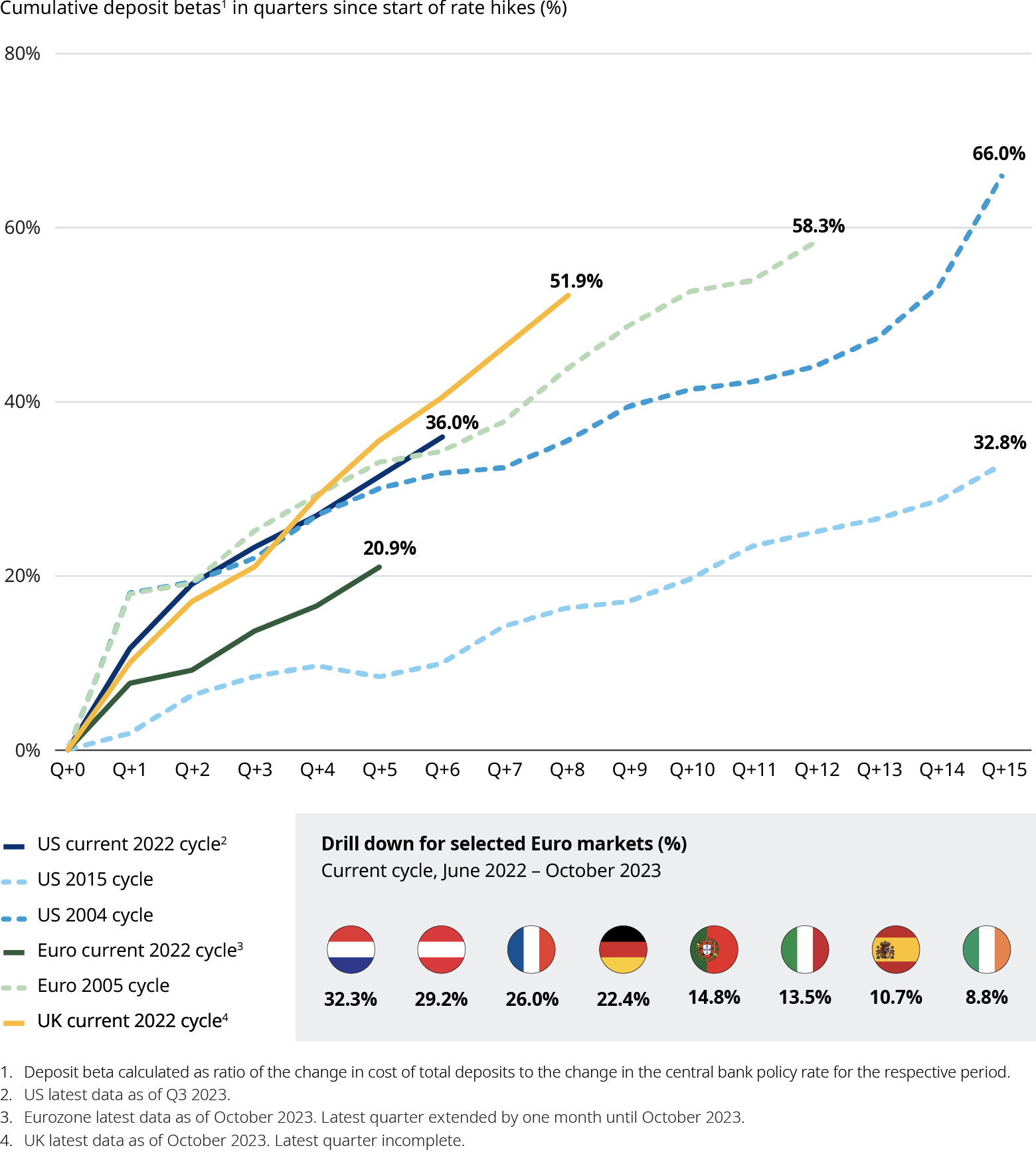
After a decade of negative or zero interest rates, European economies entered a rising rate cycle in 2022. Many banks have been able to raise rates on lending assets and, by keeping deposit costs low, expand net interest margins, which have gone up by as much as 31 basis points since Q3 2022 across the EU. However, this growth has been uneven and depended on the assets and liabilities’ structure. Not all players and markets benefited from the interest rate rise.
Due to national market differences such as saving product norms, bank concentration, share of non-for-profit banks, and bank liquidity positions, some banks had to pass higher rates onto deposit holders faster than others. In many markets, expanding bank profits also stirred up controversy. Some governments like Spain and Italy imposed windfall taxes on banks to limit their interest rate gains. Some regulators have looked for levers to try to pass on rising rates to consumers, for instance the UK Financial Conduct Authority’s 14-point action plan on cash savings.
Adapting to a digitally driven market
As markets anticipate an end to rate hikes, deposit interest rates are expected to eventually catch up. Are Europe’s banks ready to compete for deposits in an environment new to a whole generation of bankers? After years of low interest rates, has the “deposit muscle” atrophied at some institutions?
Additionally, a new generation of digitally savvy, hyper-connected clients used to immediate online transfers will be seeking better returns on their savings. The competition for deposits is only going to get tougher. The recent events with US regional banks have shown that customer behavior has changed since the previous period of high rates. Finally, the deposit product range has become more complex. Clients have access to a wider array of competing types of investments, particularly through online brokers, which they view as attractive alternatives to traditional deposits.
In this environment, a systematic approach to deposit management will be a critical value driver and necessary defensive tool. Our experience suggests that smart, analytically driven approaches can optimize deposit costs by 10-15%, or by €29 to €43 billion per year for European banks. These tools are also essential to meeting assets and liability management (ALM) and liquidity objectives, and to build the understanding needed to ensure fair treatment of each customer segment.
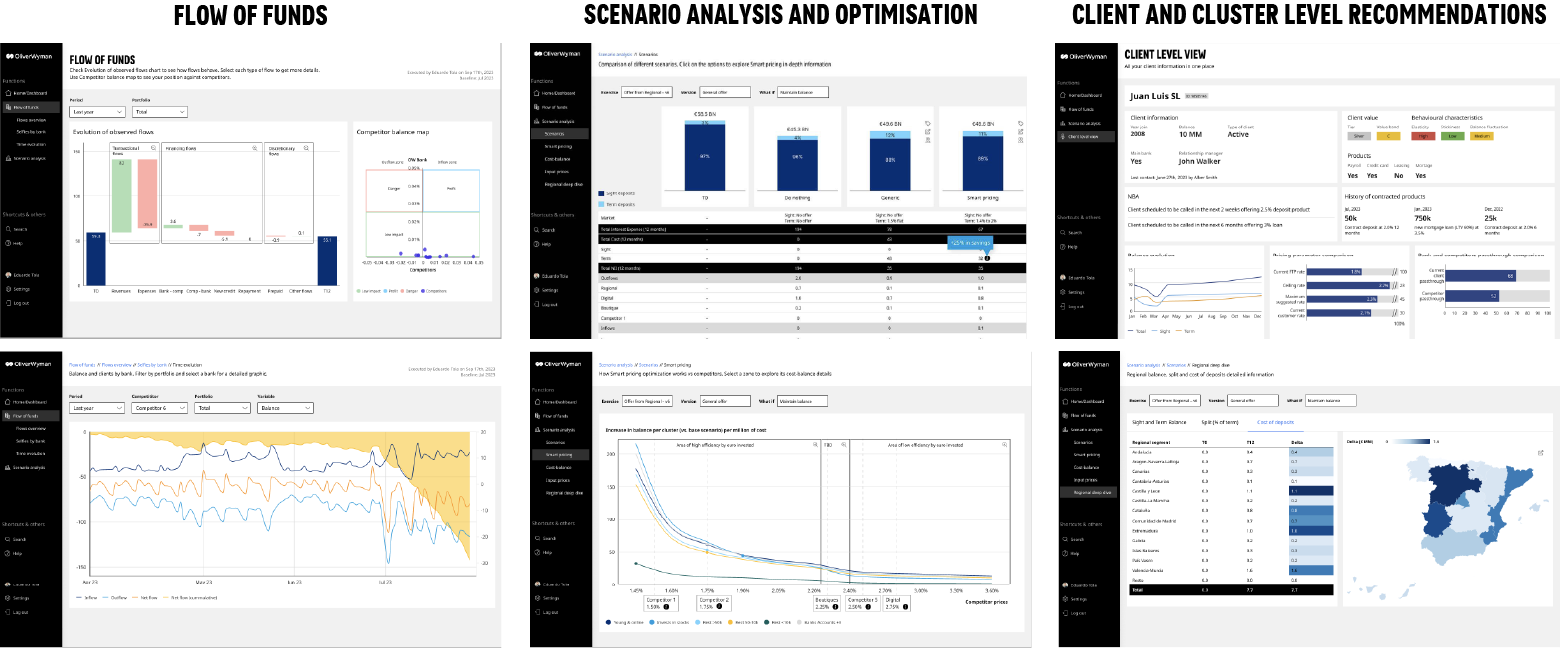
Getting deposit management in shape
Smart deposit management based on analytics and well embedded in commercial day-to-day operations will mark the difference between banks’ performance as interest rates are increasingly passed on to clients.
Oliver Wyman has worked with banks across the world to enhance their deposit management capabilities. Below, we have outlined 10 emerging best practices to assist European banks looking to understand what the competitive landscape will look like in future. We have also provided tools to help banks identify any deposit management gaps. The capabilities can be categorized broadly into two groups: analytical and operational.
Analytical capabilities to mitigate deposit management gaps
Capability 1. Flow-of-funds monitoring
Leading banks can analyze customers’ flows-of-funds across transaction categories and segments, and update this at least weekly. This allows the bank to differentiate between flows driven by their own initiatives and those resulting from competitors’ action. In the early months of the rate rise cycle, one bank client was able to monitor the impact on its deposit base following the launch of a competitor’s retail client acquisition campaign aimed at “new money.” The bank discovered that its rival’s campaign was in fact driving inflows from shared customers, who were offended by the competitor’s selective remuneration. This insight was used to improve product design, as well as to determine the timing and scope of the bank’s own pricing actions.
Capability 2. Price sensitivity and elasticity predictive models
Price sensitivity and elasticity models are key building blocks for scenario analysis and smart pricing. Analysis of patterns in the behavior of clients can be based on flow-of-funds data. These models allow banks to differentiate current and potential clients according to their sensitivity to prices and willingness to move funds in response to better deposit offers from competitors or yields of other investments. Some banks complement actual pricing and funds flow data with customer surveys to anticipate behaviors in a rate environment for which representative data is not available. One Oliver Wyman client used a combination of customer characteristics, including its products usage and digital interactions with the bank, in tandem with insights extracted from the flow-of-funds algorithm, like customers’ transactions profile and whether they have accounts with other banks, to construct a powerful price sensitivity clustering model of its retail customers.
Capability 3. Behavioral models adapted to the new cycle
These models should capture changes in customer behavior in the current interest rates cycle, assessing the expected stability and duration of deposits, especially non-maturing deposits. This understanding is key for evaluating deposits’ value, their impact on the bank’s ALM position, and eventual steering of the deposit book. Supervisors are monitoring the adequacy of these models to the new conditions. In one instance, we observed stable differences of over 100% in the behavioral tenor of deposits with the same contract term across small business customer segments, leading to 80 bps variations in deposit value.
Capability 4. Scenario analysis and optimization
By integrating granular deposit portfolio data with sensitivity and elasticity models, banks can predict deposit balances and costs under different macroeconomic and competitive scenarios. Many industry leaders leverage this capability to run what-if analyses for a range of scenarios. They even use it to build optimization engines to determine optimal prices under defined objectives and constraints.
Capability 5. Pricing deposits in a smart and differentiated way
Using price sensitivity and elasticity models along with customer value metrics, analytics-based deposit pricing recommendations can be created at the customer segment level. These tools can be deployed while considering the commercial objectives of the bank, as well as consumer protection and fairness principles. For instance, they can help design products that encourage healthy saving habits or create special offers for consumers with moderate or lower incomes.
Leading banks can develop pricing recommendations at the individual client level for larger accounts. Advanced banks are integrating these deposit pricing recommendations with their Next-Best-Action methodology and embedding this into their commercial processes.
Operational capabilities for effective deposit management
Capability 6: Wargaming
Already a common practice in other aspects of banking, wargaming is now being used to inform deposit decision-making. This process brings together executives responsible for customer segments, sales, product development, pricing, financial planning and control, and ALM. These teams collaborate to explore scenarios, analyze and discuss insights from analytics, and refine response playbooks. Scenario analysis and optimization analytics (refer to Capability 4) complement wargaming by offering realistic pricing and product response strategies. In the scenario of a deposit war, should we aim to be “first movers,” “fast followers,” or “do nothing”? How much will a retention strategy compared with a balance acquisition strategy cost us? How will each strategy impact balances and net interest income?
Capability 7: Deposits control room
Leading banks prioritize the establishment of a task force dedicated to deposit management. This task force is equipped with the necessary data to make informed decisions in a timely manner. At a minimum, this data should include the evolution of the deposits book and flows, the impact of marketing campaigns and pilots, and the projected outcomes of various scenarios. Such practices support timely, fact-based decision-making when protecting deposit balances is critical. For some of our clients, weekly or even daily flow-of-funds dashboards delivered to the control room, discussed, and actioned upon, played a crucial role to help them navigate heated periods of a “deposits war.” Armed with these tools, these banks were able to react with speed and precision to prevent deposit flight.
Capability 8: Channel and customer journey functionality
All the insight in the world is of no use without the capability to deliver differentiated deposit pricing to clients at the right time through appropriate channels. This is why industry leaders are proactively developing the technology and processes required to support deposit pricing actions for relevant segments, and then linking these up to the decisions or events that trigger them. One client, with the support of its analytics, identified a segment of valuable but price sensitive customers. As an initial step, it implemented a program of proactive retention calls by relationship managers with special offers in an effort to incentivize these customers to stay with the bank. The banks also introduced retention prompts in its mobile app for when these customers initiated large transfers to rival banks.
Capability 9: Salesforce analytics
Banks with “high-touch” segments and offerings are equipping their relationship managers with the tools to access and utilize insights from deposit analytics. Relationship managers can integrate these insights into their customer interactions and negotiations. Key components of success include an easy-to-understand methodology, training, and user-friendly front-line tools that provide price recommendations and data.
Capability 10: A test-and-learn approach
Pilots and in-market experiments are common techniques across the banking industry. Players with advanced pricing practices can take things a step further by piloting differentiated commercial actions and strategies. They can closely monitor results for test and control groups, incorporate new data back into models, and then roll out successful initiatives in a much more targeted way.
Maximize deposit management capabilities for competitive advantage
The described capabilities can be implemented with various degrees of sophistication. Most banks would already have some deposit management elements in place, such as behavioral models and a certain level of coordination between teams in planning and commercial execution. Banks in the early stages of this journey can achieve position results with simpler initial versions. More advanced players with millions of clients and tens of billions of deposits on their books must aim for advanced capabilities if they want to gain a competitive edge in deposit management.
Many institutions can expect to see their net interest income peak for this part of the cycle in 2023 as central bank rate hikes end, lending rates stop their growth, and deposit rates catch up. Banks shouldn’t wait for their competitors to start paying high deposit prices to capture their clients. In fact, recent analysis suggests that winning back lost funds can be twice as costly as retaining them in the first place. Moreover, the negative perception that loyal customers are not being treated fairly can damage the client franchise.
Deposit management capabilities will serve banks both in a flat as well as declining rate environment. These tools help banks navigate and slow down the margin squeeze while retaining and acquiring new deposit balances. The positive momentum in net interest income presents an excellent opportunity for banks to strengthen their deposit management muscle and prepare for the more intense competition that is coming.
Additional contributors include: Chris Allchin, Élie Farah, Emilio Casero, and Eduardo Tola.
