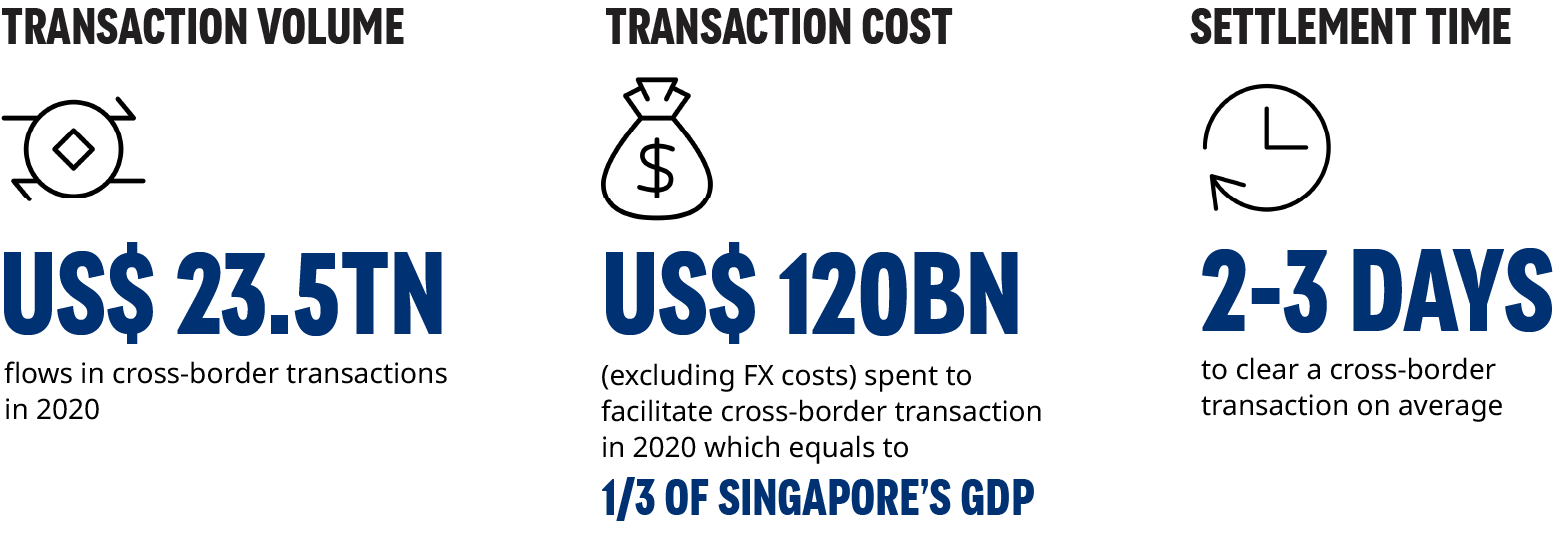
Global corporates move nearly $23.5 trillion across countries annually, equivalent to about 25% of global GDP. To do this, they have to rely on wholesale cross-border payment processes which remain sub-optimal from a cost, speed, and transparency standpoint. Aside from incurring transaction costs of more than $120 billion per annum (excluding FX costs), these processes also have additional hidden costs arising from trapped liquidity and delayed settlements.
While there have been several initiatives in recent years led by private firms, commercial banks, and central banks to overcome the challenges, a scalable and seamless solution that can work across countries, currencies, and payment systems remains elusive.
This joint research report with J.P. Morgan explores the potential of a multi-currency central bank digital currency (mCBDC) network as an effective blueprint to tackle these problems simultaneously and to introduce greater efficiencies to wholesale payments occurring across borders.
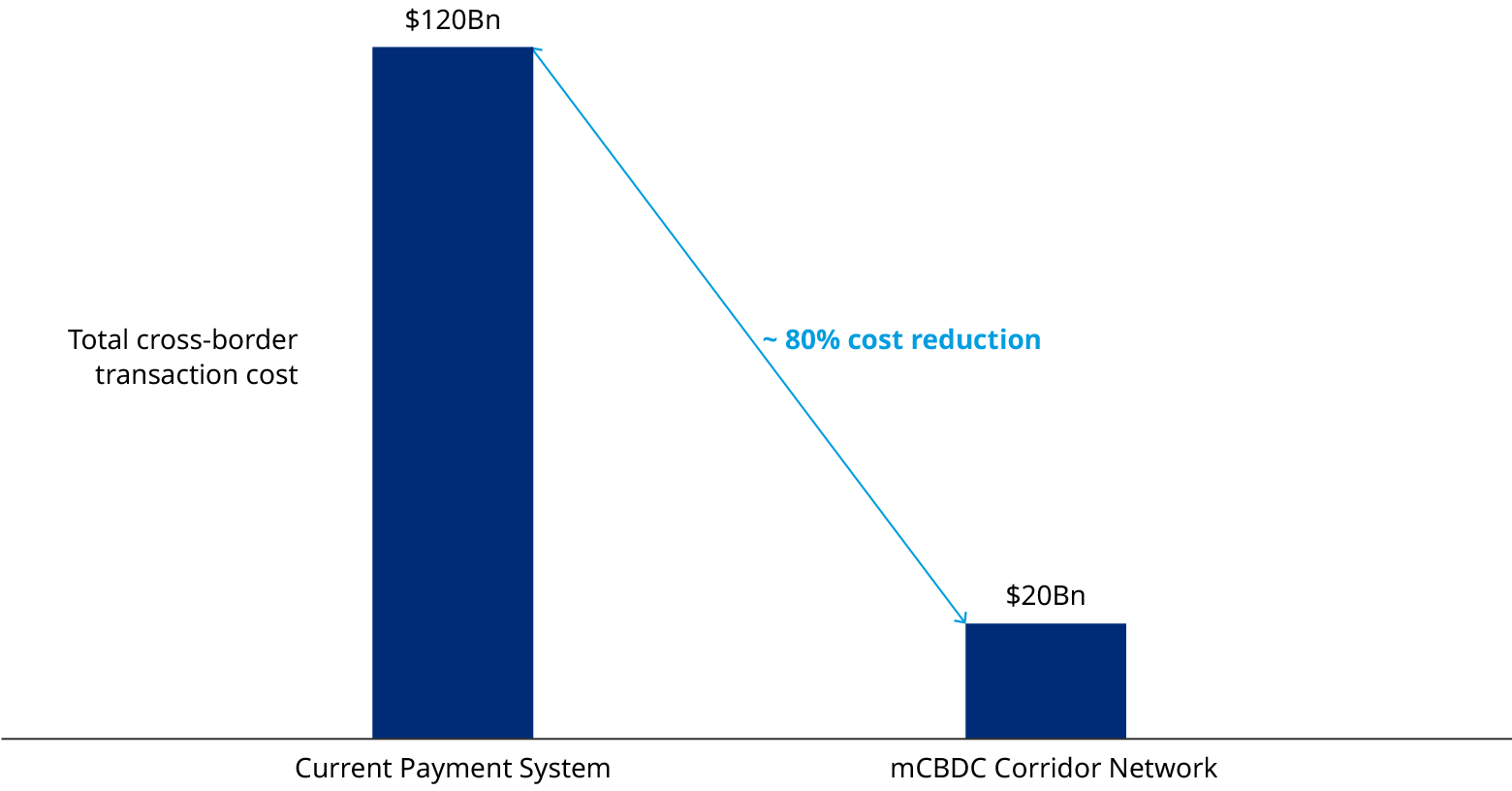
A full-scale mCBDC network has the potential to reduce the cross-border transaction revenue by around 80% annually - approximately $100 billion annually (excluding FX revenues).
 I’m convinced that CBDCs could bring transactional cash management to the next level from the standpoint of Accessibility (being able to access liquidity in their accounts without cut-offs), Convertibility (being able to convert to different currencies at will, enabling them to manage liquidity in smaller sets of currencies), Reachability (beyond just bank accounts), and Traceability (being able to have a clean trail of funds).Head of Cash Management, Global Technology MNC
I’m convinced that CBDCs could bring transactional cash management to the next level from the standpoint of Accessibility (being able to access liquidity in their accounts without cut-offs), Convertibility (being able to convert to different currencies at will, enabling them to manage liquidity in smaller sets of currencies), Reachability (beyond just bank accounts), and Traceability (being able to have a clean trail of funds).Head of Cash Management, Global Technology MNC
While the mCBDC-based corridor network challenges the traditional correspondent banking system, it also provides opportunities for the present participants - commercial banks, payment operators, market makers, and liquidity providers - to add new capabilities, and welcome new participants such as technology and other third-party service providers.
This report outlines four critical elements required for mCBDC implementation:
- the key design considerations covering data and privacy, technology and interoperability, and functionalities such as credit extension
- the building blocks, from minting and redeeming of CBDCs to FX conversion and settlement
- the roles and responsibilities of central banks, commercial banks, service providers, etc.
- the governance framework


